CNC machines have revolutionized the manufacturing industry by automating precision tasks that once required skilled labor. Understanding how these machines work not only demystifies the technology but also highlights their role in enhancing efficiency and accuracy in production. This article explores the inner workings of CNC machines, their components, and the processes that make them essential tools in modern manufacturing.
Understanding CNC Machines
CNC machines, or Computer Numerical Control machines, automate manufacturing processes using programmed commands. These machines execute precise movements, allowing for the production of intricate parts and components. With the rise of online CNC machining, businesses now have the convenience of accessing high-quality machining services remotely. This approach enables manufacturers to upload designs, specify requirements, and receive expertly crafted parts without the need for on-site operations.
Key Components of CNC Machines
- Controller: The core of the CNC machine receives instructions from the computer and converts them into signals that guide the machine’s movements.
- Drive System: This system consists of motors and gears that enable the machine to move along various axes, typically X, Y, and Z.
- Cutting Tool: The tool, which can vary based on the material and design needs, removes material from the workpiece to achieve the desired shape.
- Worktable: The surface where the material is secured during the machining process, ensuring stability and accuracy.
CNC Machining Process
- Programming: Operators input design specifications using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software, translating the design into a machine-readable format.
- Material Setup: The material is placed on the worktable and secured using clamps or fixtures.
- Tool Path Generation: The CNC controller calculates the optimal path for the cutting tool based on the input data.
- Execution: The machine implements the programmed instructions, with the cutting tool moving along designated paths to shape the material.
- Precision: CNC machines deliver consistent accuracy in machining, which manual methods can’t achieve.
- Efficiency: Automation speeds up production cycles, enabling higher output in less time.
- Flexibility: Operators can quickly change designs and specifications, allowing for different projects without extensive downtime.
CNC machines play a critical role in modern manufacturing, providing manufacturers with tools that improve productivity and maintain high-quality standards.
The Basic Components of CNC Machines
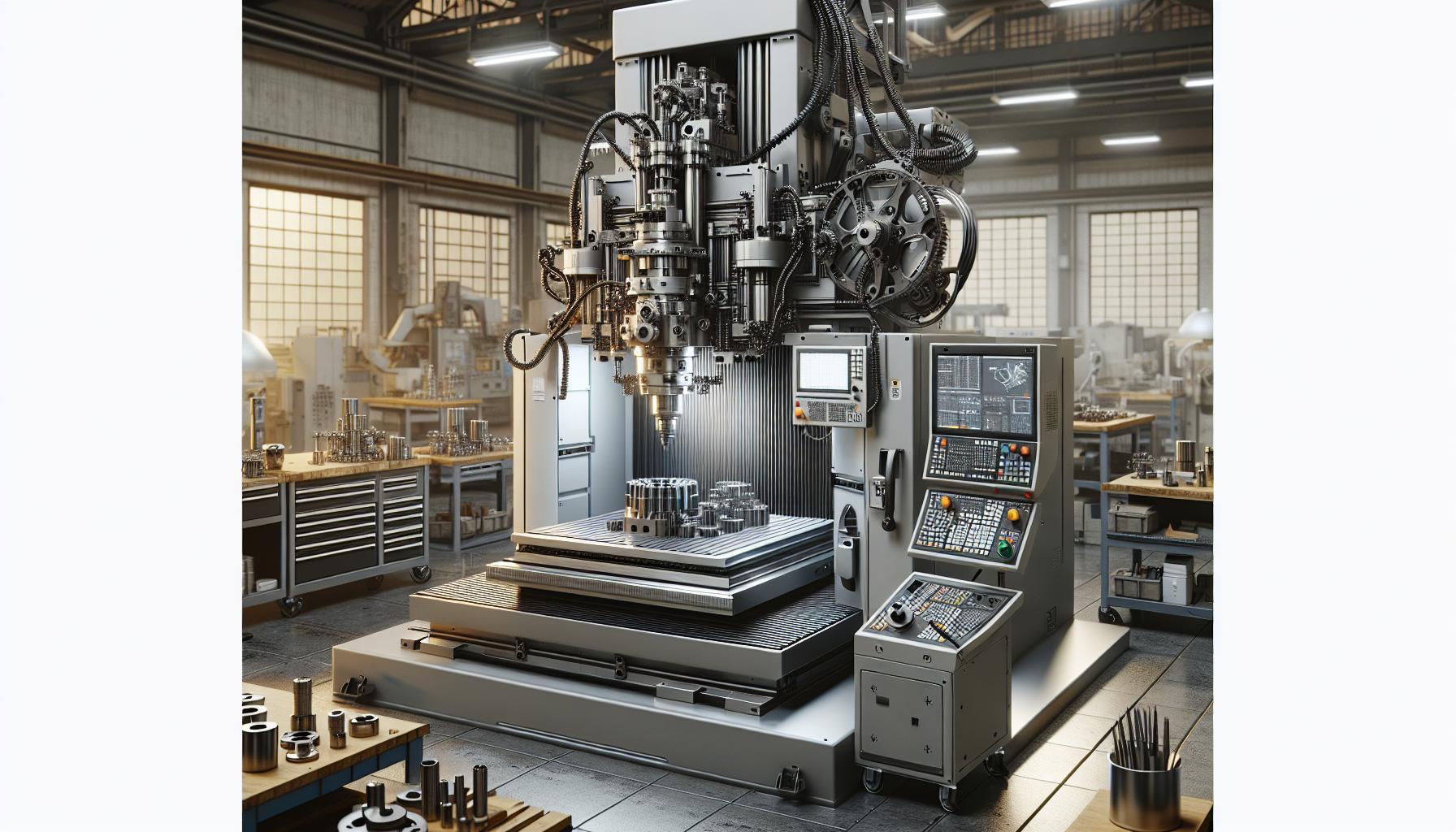
CNC machines consist of several essential components that work together to execute precise manufacturing tasks effectively. Understanding these components is crucial for grasping how CNC machines operate.
Control System
The control system serves as the brain of the CNC machine. It interprets the programmed instructions and translates them into signals to control the machine’s movements. The system typically includes a computer or microcontroller that processes G-code, the standard language for CNC programming. Operators can input design specifications through CAD software, allowing for seamless transitions from design to production.
Drive Mechanism
The drive mechanism is responsible for the movement of the CNC machine along specified axes. This system includes motors, usually stepper or servo motors, that provide the necessary power and precision. The movement occurs along the X, Y, and Z axes, enabling the CNC machine to reach various points within the working envelope. This precise movement ensures accuracy when shaping materials.
Machine Tool
The machine tool is the component that interacts directly with the material being machined. It can include various cutting tools, such as drills, lathes, or mills, depending on the desired operation. The machine tool’s design and configuration influence the efficiency and quality of the cutting process. Proper tool selection is critical for achieving optimal results and minimizing material wear.
The CNC Machining Process
The CNC machining process involves several steps to ensure accuracy and efficiency in part production. Each phase contributes to the overall functionality of CNC machines.
Design and Programming
Design and programming form the foundation of CNC machining. Designers create models using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software, which allows for precise specifications of parts. Once designs are finalized, they convert into Machine Code, typically G-code, that instructs the machine. The programming phase includes inputting commands that outline specific actions, such as tool selection, movement speed, and machining paths.
Tool Path Calculation
Tool path calculation determines the optimal route for the cutting tool. The process begins with analyzing the part’s geometry to establish an effective path that minimizes machining time while maintaining quality. Software algorithms take parameters like tool diameter, material characteristics, and desired finish into account. Accurate tool path generation reduces wear on the tools and maximizes machining efficiency.
Operation of CNC Machines
Operation of CNC machines involves executing the pre-programmed instructions. After setup, the machine follows the G-code to move the cutting tool along designated paths. The control system coordinates all movements, ensuring exact positioning based on the programmed design. Feedback mechanisms monitor the cutting process, adjusting speeds and pathways in real-time to ensure optimal performance. Throughout this process, the workpiece remains securely clamped to the worktable, allowing for stability and precision during machining.
Types of CNC Machines
CNC machines come in several distinct types, each designed for specific manufacturing processes. Understanding the types helps in selecting the right machine for a particular application.
Milling Machines
Milling machines use rotating cutting tools to remove material from a workpiece. They perform a variety of tasks, such as drilling, boring, and shaping materials. CNC milling machines can operate on multiple axes, allowing for complex shapes and precision cuts. Horizontal and vertical configurations serve different machining needs, with vertical mills generally preferred for their versatility.
Lathes
Lathes shape material by rotating the workpiece against a stationary cutting tool. CNC lathes improve traditional lathes by automating the process, ensuring consistent quality. They excel at creating cylindrical parts and detailed profiles, used in industries like automotive and aerospace. The ability to perform multiple operations in one setup offers efficiency and precision.
Laser Cutters
Laser cutters utilize focused beams of light to slice through materials with high accuracy. CNC laser machines offer extreme precision and are effective for cutting various materials, including metals, plastics, and wood. Their speed and clean cuts minimize post-processing requirements, making them ideal for detailed designs. Laser technology also allows for engraving and marking, expanding their functionality in production.
Conclusion
CNC machines have revolutionized the manufacturing landscape by enhancing precision and efficiency. Their ability to automate complex processes allows businesses to produce high-quality components with minimal human intervention.
With a deep understanding of their components and operational processes, manufacturers can optimize production workflows and adapt to changing design requirements swiftly.
As technology continues to advance, the role of CNC machines will only grow, making them indispensable tools in modern manufacturing. Embracing this technology not only boosts productivity but also sets the foundation for innovation in design and production.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are CNC machines?
CNC machines, or Computer Numerical Control machines, are automated devices that use programmed commands to control their movements. They can produce intricate parts with high precision by following detailed instructions, significantly enhancing efficiency in manufacturing processes.
How do CNC machines operate?
CNC machines operate by interpreting design specifications programmed through CAD software. These instructions are converted to Machine Code (G-code), which guides the machine’s movements, enabling it to cut or shape materials according to precise specifications.
What are the key components of a CNC machine?
Key components of a CNC machine include the controller (interprets instructions), the drive system (enables movement along axes), the cutting tool (shapes material), and the worktable (holds the material during machining). Each part plays a vital role in achieving precise outcomes.
What is the CNC machining process?
The CNC machining process involves several steps: designing the part using CAD software, generating G-code, calculating tool paths for efficiency, setting up the material, and executing programmed instructions for precise machining. Each step is crucial for maintaining quality and accuracy.
What types of CNC machines are there?
Common types of CNC machines include CNC milling machines (for drilling and shaping), CNC lathes (for creating cylindrical parts), and CNC laser cutters (for precise cutting and engraving). Each type is suited for specific applications within the manufacturing industry.
